Kyverno - A Kubernetes native policy manager (Policy as Code)
Problem Statement
While working with the Kubernetes cluster, there are many problem statements such as -
- If one of the applications is having really high CPU & memory utilization, how the other applications will run?
- A user is changing the default network policies which can result in open gates to the attackers. How can we prevent that?
- Developers are not using the best practices for the applications such as using the latest tags for the docker images. Checking if we are putting the proper configuration to the k8s resources according to the need to project.
How can we tackle such situations? How can we put policies to the cluster? 🤔
Solution
To handle such situations, we can enforce a policy management solution to the Kubernetes cluster that can handle many problems related to policies.
There are many policy management solutions are available such as OPA Gatekeeper but there is a cloud-native solution available for k8s i.e. Kyverno (https://kyverno.io/)
Kyverno Overview
Kyverno is a policy engine designed for Kubernetes. With Kyverno, policies are managed as Kubernetes resources and no new language is required to write policies. This allows using familiar tools such as kubectl, git, and kustomize to manage policies.
Kyverno policies can perform the following operations on generated Kubernetes resources-
- Validation
- Mutation
- Generation
The Kyverno CLI can be used to test policies and validate resources as part of a CI/CD pipeline.
For more information - https://kyverno.io/docs/introduction/
Kyverno Installation
Prerequisites
To install Kyverno, we need a functional Kubernetes cluster. For this purpose, we can either use local k8s clusters such as Minikube, Kind etc. or any cluster running on the cloud.
Kyverno can be installed using the installation methods mentioned at https://kyverno.io/docs/installation/
Helm Installation
In order to install kyverno using helm, perform the following steps:
- Add the Kyverno helm repository
helm repo add kyverno https://kyverno.github.io/kyverno/
- Scan the helm for the latest charts for Kyverno
helm repo update
- For the kyverno version ≥
1.4.2, we need to add kyverno-crds separately before installing the kyverno
# Add Kyverno-crds
helm install kyverno-crds kyverno/kyverno-crds --namespace kyverno --create-namespace
# Install Kyverno
helm install kyverno kyverno/kyverno --namespace kyverno
- For the kyverno version <
1.4.2, you can directly install the kyverno without the kyverno-crds.
# Install Kyverno
helm install kyverno kyverno/kyverno --namespace kyverno
YAML Installation
If you want to install the kyverno without Helm directly using manifest, we can deploy the latest release using the following command
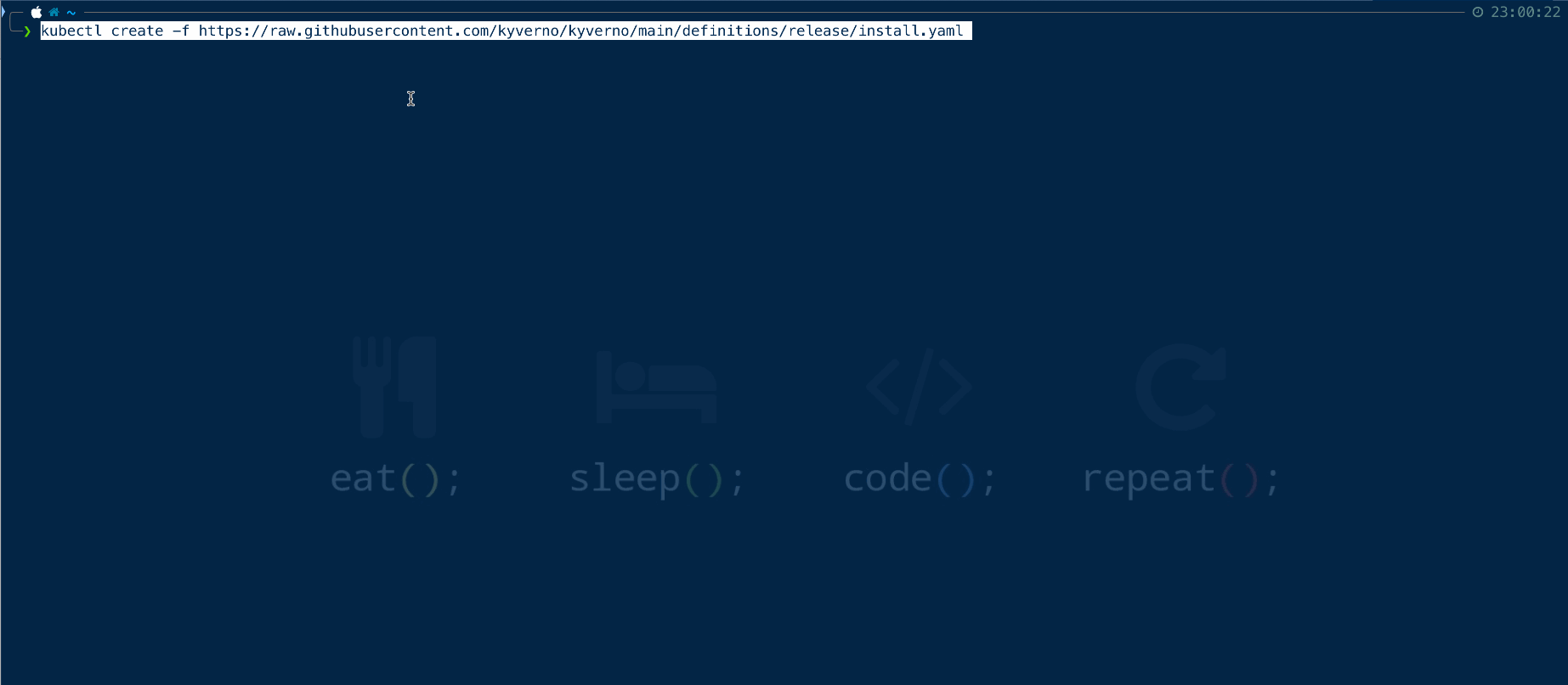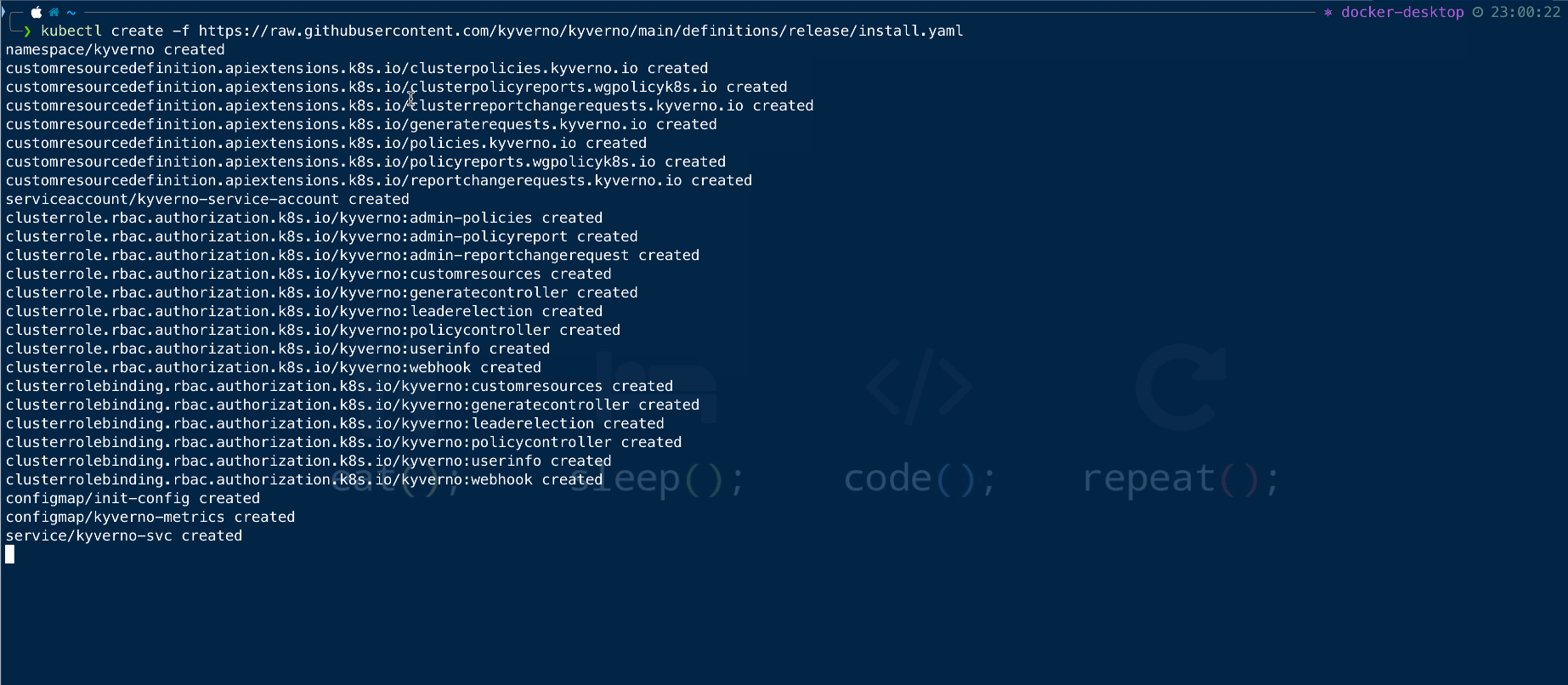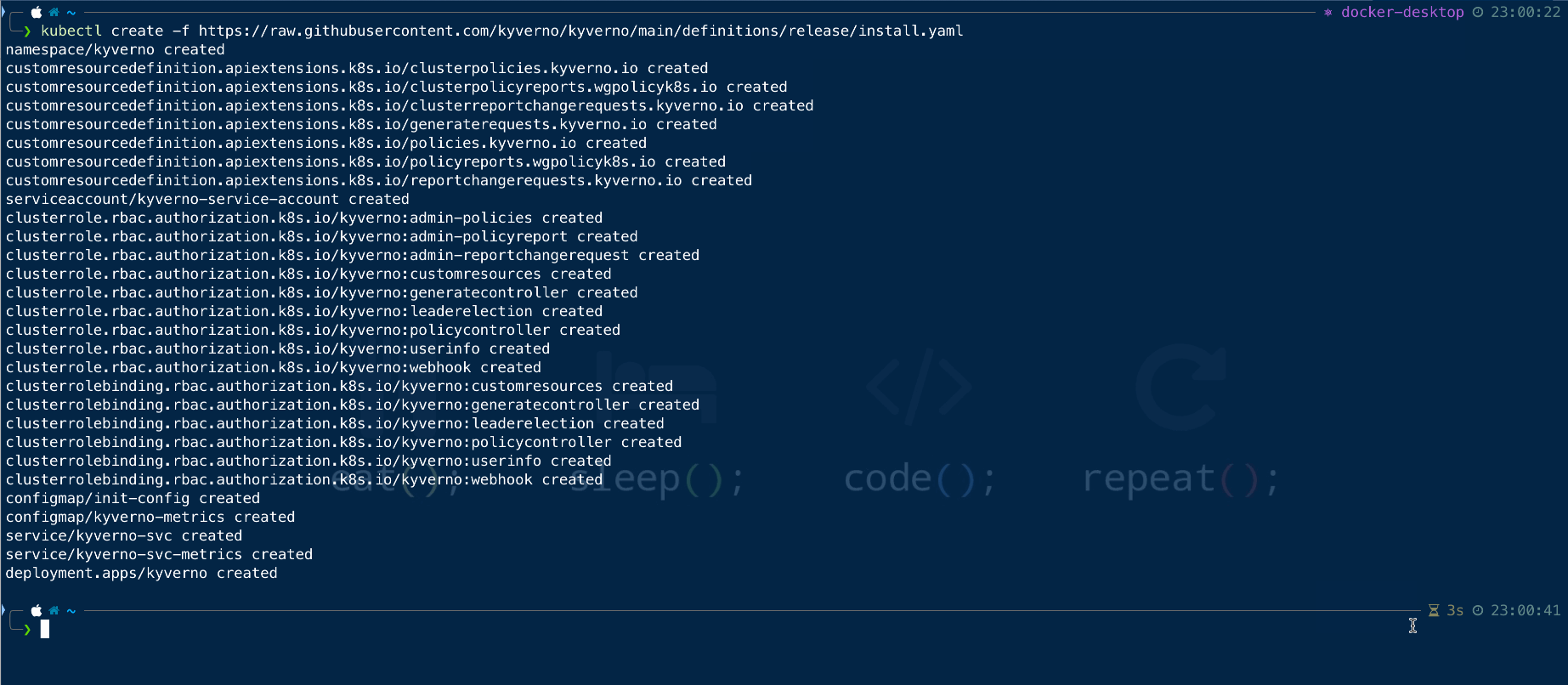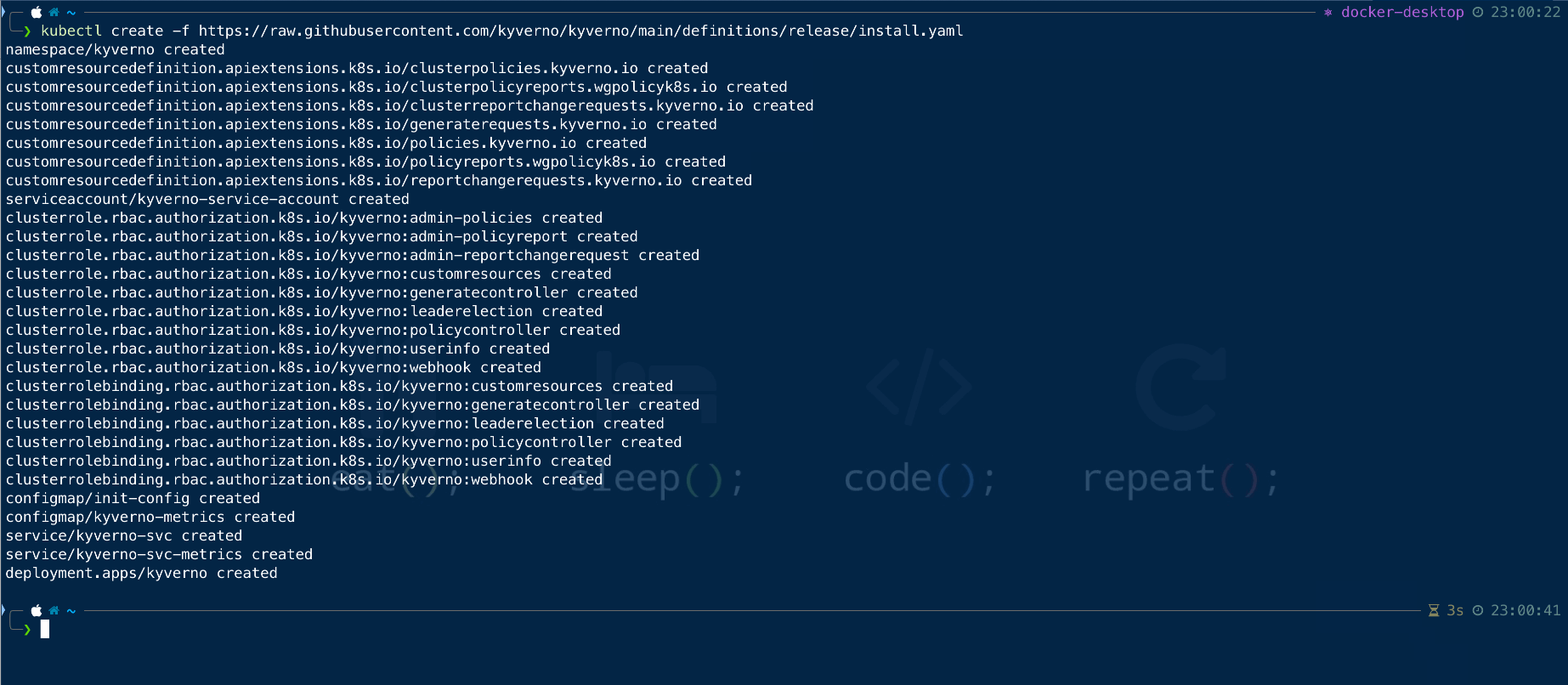
kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kyverno/kyverno/main/definitions/release/install.yaml
Kyverno Operations
Let's have a deeper look into the operations that can be performed using Kyverno.
Validation
Using validation, we can tackle the situation such as high CPU, memory usage or avoid altering default network policies etc. We can apply the kyverno policy to do such validation.
Here is the sample ClusterPolicy definition to avoid creating k8s resource, if resource definitions are not defined -
## Policy to warn over resource limits. It is always recommended defining resource limits.
## https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/#requests-and-limits
apiVersion: kyverno.io/v1
kind: ClusterPolicy
metadata:
name: require-requests-limits
namespace: caas-policies
annotations:
policies.kyverno.io/title: Require Limits and Requests
policies.kyverno.io/category: Multi-Tenancy
policies.kyverno.io/severity: medium
policies.kyverno.io/subject: Pod
policies.kyverno.io/description: >-
As application workloads share cluster resources, it is important to limit resources
requested and consumed by each Pod. It is recommended to require resource requests and
limits per Pod, especially for memory and CPU. If a Namespace level request or limit is specified,
defaults will automatically be applied to each Pod based on the LimitRange configuration.
This policy validates that all containers have something specified for memory and CPU
requests and memory limits.
spec:
background: true
validationFailureAction: enforce
rules:
- name: validate-resources
match:
resources:
kinds:
- Pod
exclude:
resources:
namespaces:
- "caas-*"
- "flux-*"
validate:
message: >-
You have not defined the container requests and limits. This might cause the
issue with other application. CPU and memory resource requests and limits
are required.
Reference - https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/assign-cpu-resource/
pattern:
spec:
containers:
- resources:
requests:
memory: "?*"
cpu: "?*"
limits:
memory: "?*"
Once this policy will be applied, no one cannot create any Kubernetes resources without the resource definitions for the containers. This will avoid the over utilization of a single application.
More kyverno validation policies can be found here — https://kyverno.io/policies/?policytypes=validate
Mutation
Using mutation, we can modify the resources if a certain condition matches. For example, we can change the imagePullPolicy to Always if the image tag is latest.
apiVersion: kyverno.io/v1
kind: ClusterPolicy
metadata:
name: always-pull-images
annotations:
policies.kyverno.io/title: Always Pull Images
policies.kyverno.io/category: Sample
policies.kyverno.io/severity: medium
policies.kyverno.io/subject: Pod
policies.kyverno.io/description: >-
By default, images that have already been pulled can be accessed by other
Pods without re-pulling them if the name and tag are known. In multi-tenant scenarios,
this may be undesirable. This policy mutates all incoming Pods to set their
imagePullPolicy to Always. An alternative to the Kubernetes admission controller
AlwaysPullImages.
spec:
background: false
rules:
- name: always-pull-images
match:
resources:
kinds:
- Pod
mutate:
patchStrategicMerge:
spec:
containers:
- (name): "?*"
imagePullPolicy: Always
More kyverno mutation policies can be found here — https://kyverno.io/policies/?policytypes=mutate
Generation
Using generation, we can generate new resources in the Kubernetes cluster, if a condition has been met.
For example, if a new namespace is created, we might want to create ResourceQuota and LimitRange resources for the namespace.
apiVersion: kyverno.io/v1
kind: ClusterPolicy
metadata:
name: add-ns-quota
annotations:
policies.kyverno.io/title: Add Quota
policies.kyverno.io/category: Multi-Tenancy
policies.kyverno.io/subject: ResourceQuota, LimitRange
policies.kyverno.io/description: >-
To better control the number of resources that can be created in a given
Namespace and provide default resource consumption limits for Pods,
ResourceQuota and LimitRange resources are recommended.
This policy will generate ResourceQuota and LimitRange resources when
a new Namespace is created.
spec:
rules:
- name: generate-resourcequota
match:
resources:
kinds:
- Namespace
generate:
kind: ResourceQuota
name: default-resourcequota
synchronize: true
namespace: "{{request.object.metadata.name}}"
data:
spec:
hard:
requests.cpu: '4'
requests.memory: '16Gi'
limits.cpu: '4'
limits.memory: '16Gi'
- name: generate-limitrange
match:
resources:
kinds:
- Namespace
generate:
kind: LimitRange
name: default-limitrange
synchronize: true
namespace: "{{request.object.metadata.name}}"
data:
spec:
limits:
- default:
cpu: 500m
memory: 1Gi
defaultRequest:
cpu: 200m
memory: 256Mi
type: Container
This policy will generate the respective resources whenever a new namespace will be created.
More kyverno generation policies can be found here — https://kyverno.io/policies/?policytypes=generate
Hands-On
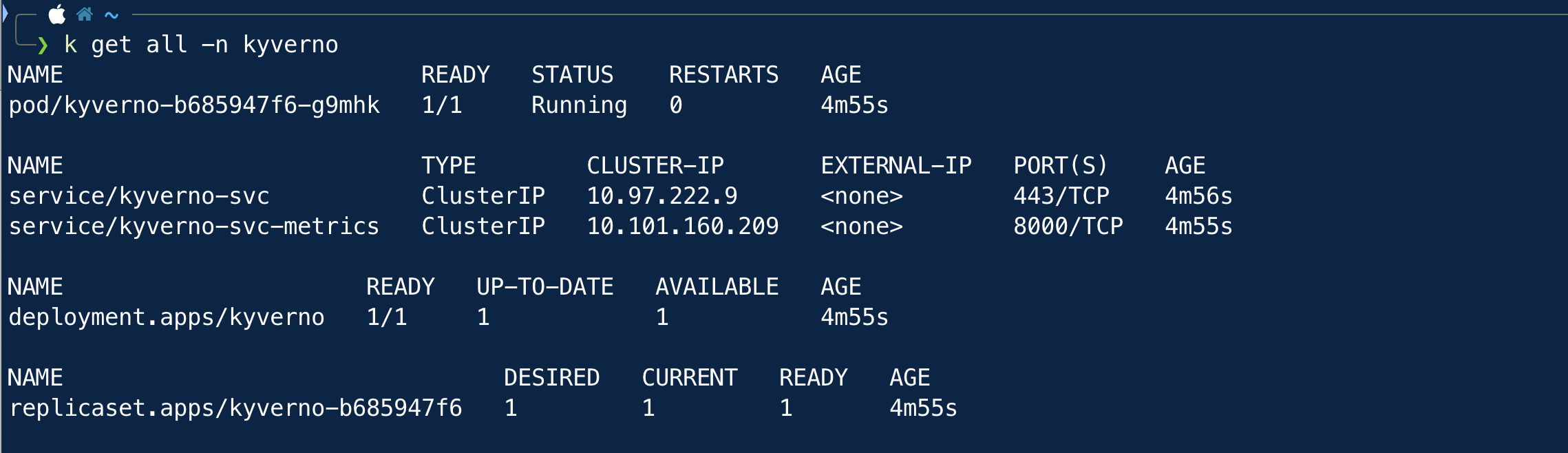
Now we will see the kyverno in action. To check whether kyverno is installed properly, check all the resources in the kyverno namespace -
Applying Policies
Once kyverno installation has been verified, we will try to create some policies and apply them to the cluster.
Now, we want to apply a policy that will disallow resource creation in the default namespace.
apiVersion: kyverno.io/v1
kind: ClusterPolicy
metadata:
name: disallow-default-namespace
annotations:
pod-policies.kyverno.io/autogen-controllers: none
policies.kyverno.io/title: Disallow Default Namespace
policies.kyverno.io/category: Multi-Tenancy
policies.kyverno.io/severity: medium
policies.kyverno.io/subject: Pod
policies.kyverno.io/description: >-
Kubernetes Namespaces are an optional feature that provide a way to segment and
isolate cluster resources across multiple applications and users. As a best
practice, workloads should be isolated with Namespaces. Namespaces should be required
and the default (empty) Namespace should not be used. This policy validates that Pods
specify a Namespace name other than `default`.
spec:
validationFailureAction: audit
rules:
- name: validate-namespace
match:
resources:
kinds:
- Pod
validate:
message: "Using 'default' namespace is not allowed."
pattern:
metadata:
namespace: "!default"
- name: require-namespace
match:
resources:
kinds:
- Pod
validate:
message: "A namespace is required."
pattern:
metadata:
namespace: "?*"
- name: validate-podcontroller-namespace
match:
resources:
kinds:
- DaemonSet
- Deployment
- Job
- StatefulSet
validate:
message: "Using 'default' namespace is not allowed for pod controllers."
pattern:
metadata:
namespace: "!default"
- name: require-podcontroller-namespace
match:
resources:
kinds:
- DaemonSet
- Deployment
- Job
- StatefulSet
validate:
message: "A namespace is required for pod controllers."
pattern:
metadata:
namespace: "?*"
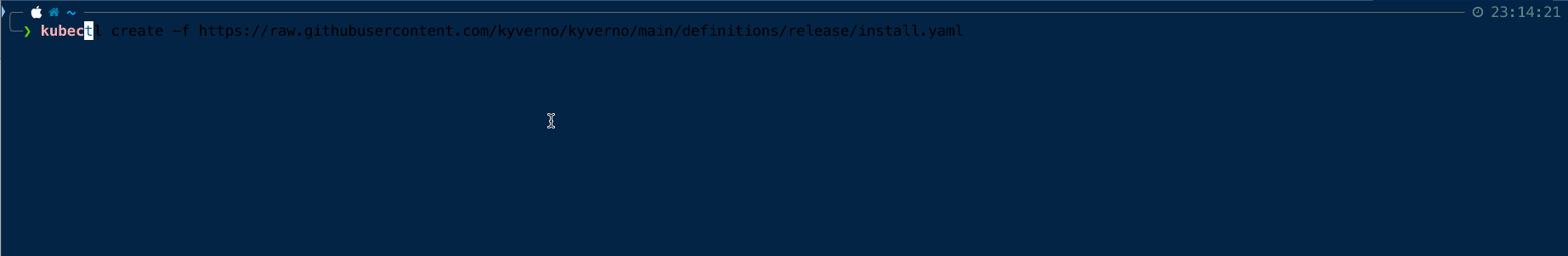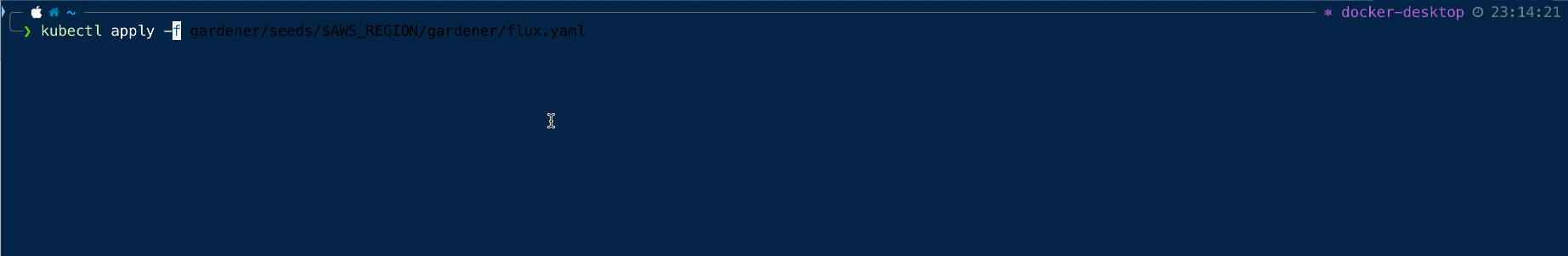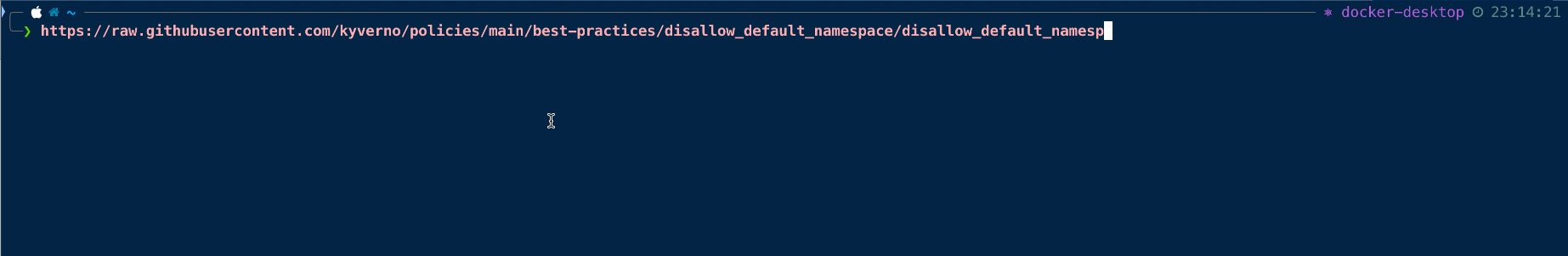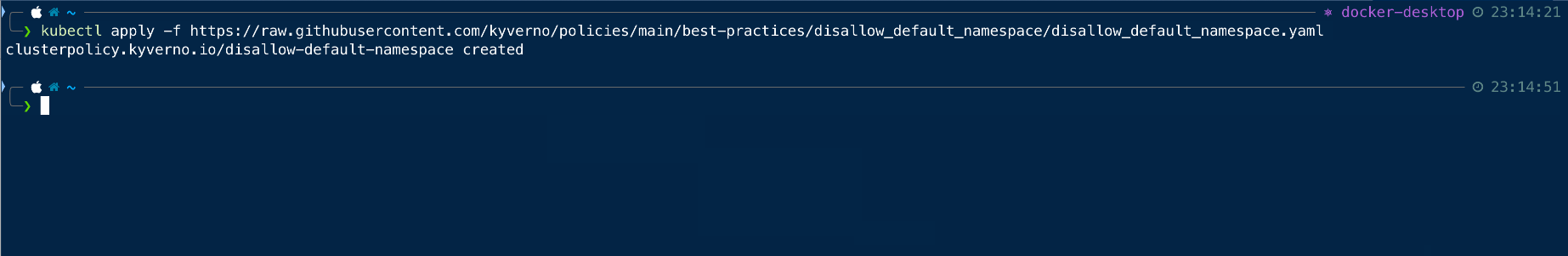
Resource Creation Testing
Once the policies are applied to the cluster, we can proceed with the testing of the resource creation.
Since we have applied the policies to ensure that no resource can be created in the default namespace, so we will try to create a pod in the default namespace.
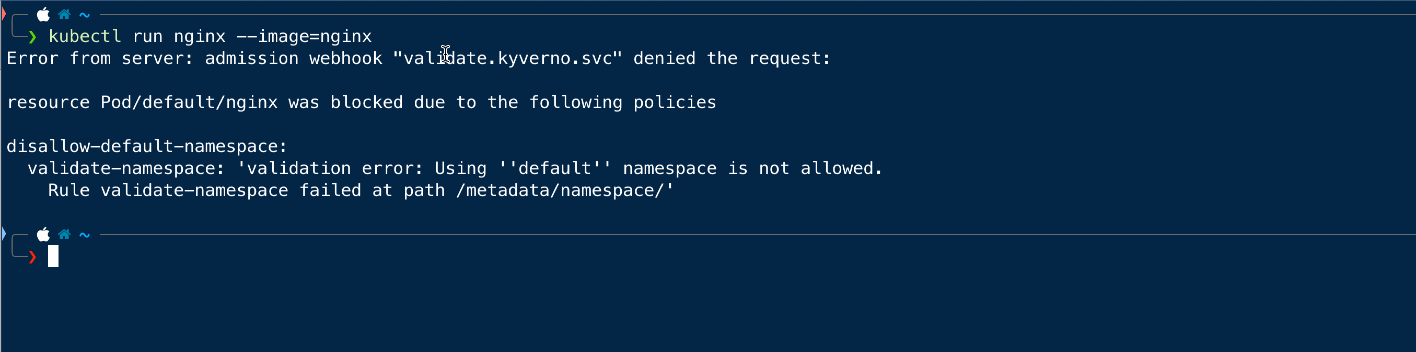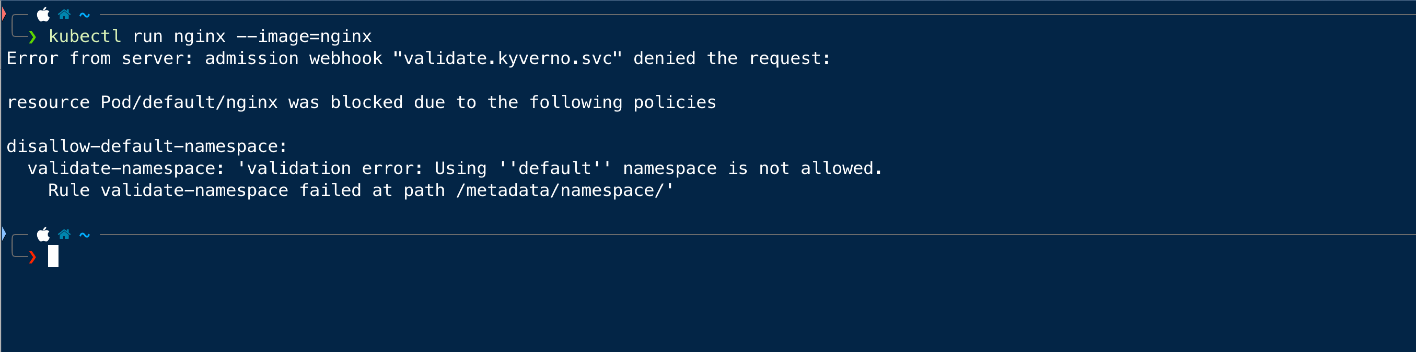
As the above error provides the information that we are not allowed to create the resource in the default namespace.
Now we will try to create the same pod in the kyverno namespace and see if that is working.
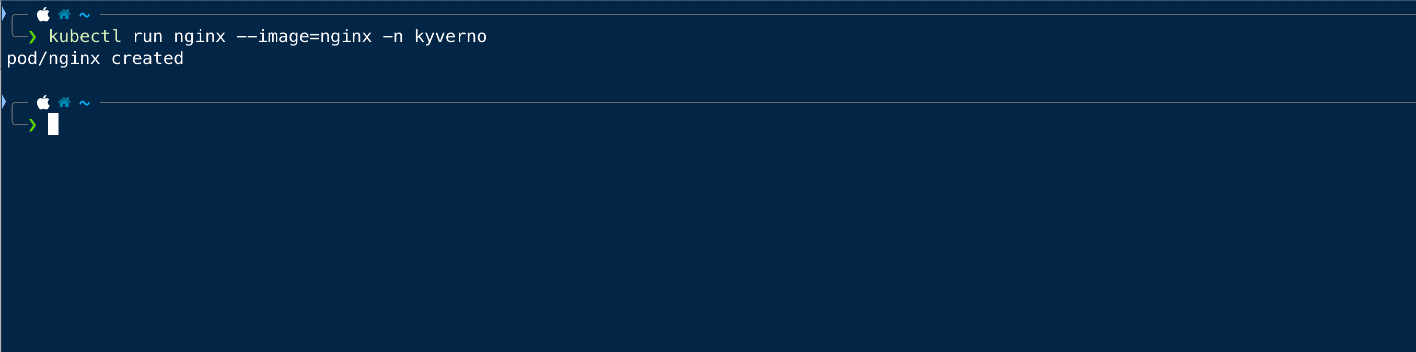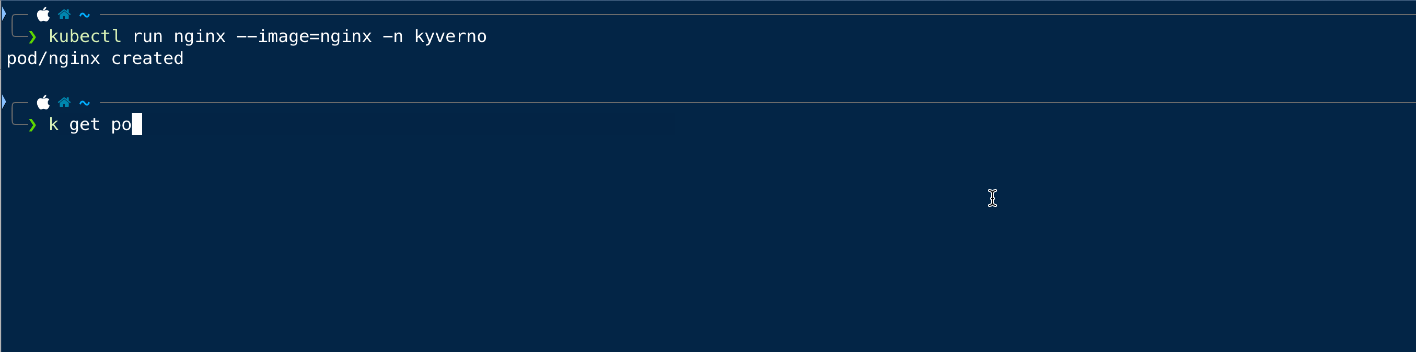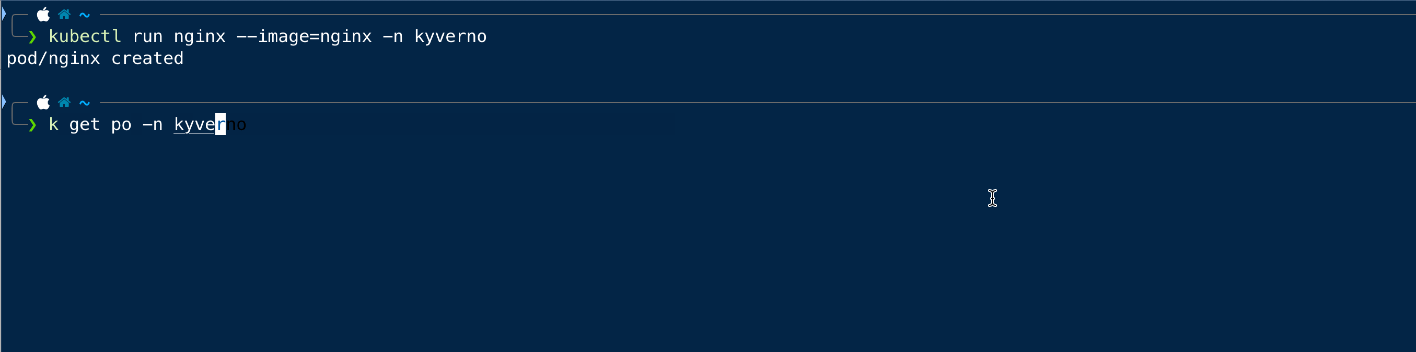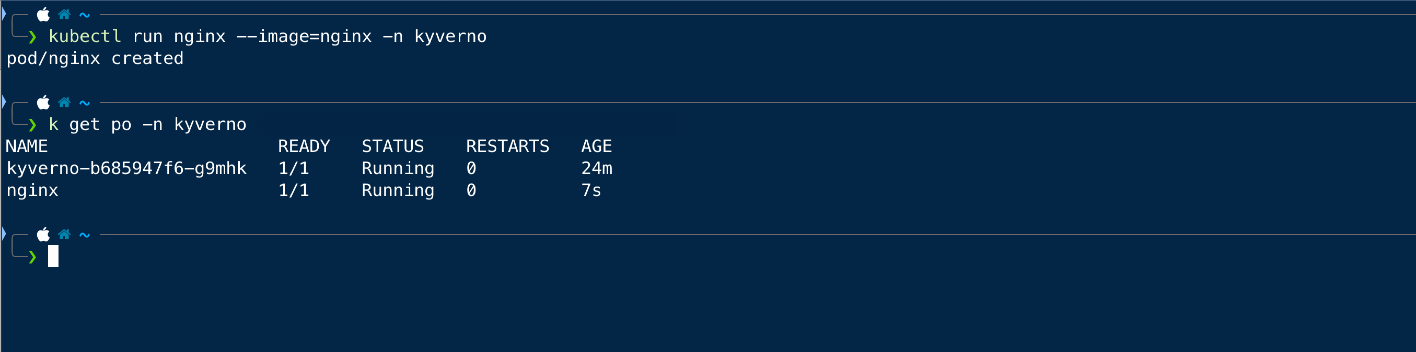
As we can see that we can create the pod in any namespace other than the default one.
Note
There is one important option while applying the policies — Validation Failure Action which provides the option how the user should be impacted if the policies are applied. If we set the value of this option to enforce then the end user will not able to create the resource while with the option audit, end user can create the resources but the warning will be logged into the events.
Reference - https://kyverno.io/docs/writing-policies/validate/#validation-failure-action
Conclusion
As we can see that Kyverno is an awesome Policy as Code or Policy Management tool that is native to Kubernetes. We can easily apply policies and best practices into our Kubernetes clusters. Since the policies are written in YAML, it is quite easy to write and come up with less complexity.
Thanks for reading. Hope you got good insights about Kyverno.